前面,我们学习了python模块的基本概念、如何安装第三方模块,并学习了写自己的模块和包。可以点这里回顾一下:
有同学问了个问题:在python里如何复制、删除、重命名文件?
有个同学知道os.system(),就回答说:
os.system('cp a.v b.v')
os.system('rm b.v')
os.system('mv a.v b.v')
那如果是windows系统呢?
有个熟悉DOS命令的同学回答说:
os.system('copy a.v b.v')
os.system('del b.v')
os.system('rename a.v b.v')
又有个同学找到一个“通用的”方法说,windows上可以安装类unix小工具,然后继续用linux的方法。
其实python已经为我们考虑过系统兼容的问题了。在python的官方网站上有以下的描述:
“Runs anywhere, including Mac OS X, Windows, Linux, and Unix, with unofficial builds also available for Android and iOS.
所以,在开始更深入的学习之前,我们有必要先来学一下基本的与操作系统(os)、文件(sys)、shell(shutil)打交道的方式。os, sys, shutil这三个模块/包是python安装时自带的,基本上能覆盖我们的需求。
研究os、sys、shutil提供了哪些函数
我们先用dir()来看看这三个模块/包提供了哪些函数,然后挑一些常用的函数介绍下。import os模块后,用dir(os)来查看os提供了哪些函数,如下(常用的用蓝色标出):
>>> import os
>>> dir(os)
[..., 'abc', 'abort', 'access', 'altsep', 'chdir', 'chmod', 'chown', 'chroot', 'close', 'closerange', 'confstr', 'confstr_names', 'cpu_count', 'ctermid', 'curdir', 'defpath', 'device_encoding', 'devnull', 'dup', 'dup2', 'environ',
'environb', 'errno', 'error', 'execl', 'execle', 'execlp', 'execlpe',
'execv', 'execve', 'execvp', 'execvpe', 'extsep', 'fchdir', 'fchmod',
'fchown', 'fdatasync', 'fdopen', 'fork', 'forkpty', 'fpathconf',
'fsdecode', 'fsencode', 'fspath', 'fstat', 'fstatvfs', 'fsync',
'ftruncate', 'fwalk', 'get_blocking', 'get_exec_path',
'get_inheritable', 'get_terminal_size', 'getcwd', 'getcwdb', 'getegid', 'getenv',
'getenvb', 'geteuid', 'getgid', 'getgrouplist', 'getgroups',
'getloadavg', 'getlogin', 'getpgid', 'getpgrp', 'getpid', 'getppid',
'getpriority', 'getresgid', 'getresuid', 'getsid', 'getuid', 'getxattr',
'initgroups', 'isatty', 'kill', 'killpg', 'lchown', 'linesep', 'link', 'listdir', 'listxattr', 'lockf', 'lseek', 'lstat', 'major', 'makedev', 'makedirs', 'minor', 'mkdir', 'mkfifo', 'mknod', 'name', 'nice', 'open', 'openpty', 'pardir', 'path', 'pathconf', 'pathconf_names', 'pathsep', 'pipe', 'pipe2', 'popen', 'posix_fadvise', 'posix_fallocate', 'pread', 'putenv', 'pwrite', 'read', 'readlink', 'readv', 'remove', 'removedirs', 'removexattr', 'rename', 'renames', 'replace', 'rmdir', 'scandir',
'sched_get_priority_max', 'sched_get_priority_min',
'sched_getaffinity', 'sched_getparam', 'sched_getscheduler',
'sched_param', 'sched_rr_get_interval', 'sched_setaffinity',
'sched_setparam', 'sched_setscheduler', 'sched_yield', 'sendfile', 'sep',
'set_blocking', 'set_inheritable', 'setegid', 'seteuid', 'setgid',
'setgroups', 'setpgid', 'setpgrp', 'setpriority', 'setregid',
'setresgid', 'setresuid', 'setreuid', 'setsid', 'setuid', 'setxattr',
'spawnl', 'spawnle', 'spawnlp', 'spawnlpe', 'spawnv', 'spawnve',
'spawnvp', 'spawnvpe', 'st', 'stat', 'stat_float_times', 'stat_result',
'statvfs', 'statvfs_result', 'strerror', 'supports_bytes_environ',
'supports_dir_fd', 'supports_effective_ids', 'supports_fd',
'supports_follow_symlinks', 'symlink', 'sync', 'sys', 'sysconf', 'sysconf_names', 'system', 'tcgetpgrp', 'tcsetpgrp', 'terminal_size', 'times', 'times_result', 'truncate', 'ttyname', 'umask', 'uname', 'uname_result', 'unlink', 'unsetenv', 'urandom', 'utime', 'wait', 'wait3', 'wait4', 'waitid', 'waitid_result', 'waitpid', 'walk', 'write', 'writev']
sys和shutil就留给同学们自己做实验了。
把研究结果整理如下
我们把函数名字看起来眼熟的整理如下。
os.name
os.getcwd
os.listdir
os.remove
os.makedirs
os.mkdir
os.rmdir
os.chdir
os.rename
os.system
os.sep
os.linesep
os.environ
os.path.abspath
os.path.dirname
os.path.basename
os.path.isfile
os.path.isdir
os.stat
os.path.split
os.path.join
os.popen
os.path.exists
os.symlink
sys.argv
sys.exit
sys.path
sys.platform
sys.stdin
sys.stdout
sys.stderr
shutil.chown
shutil.copy
shutil.copy2
shutil.copytree
shutil.disk_usage
shutil.errno
shutil.make_archive
shutil.which
只列个函数名字有什么用?怎么没有用法介绍?函数太多,我不想也不太实际为每个函数都写一段完整的用法说明和使用示例。我还是来介绍下怎么查帮助文档吧。
搞懂每个函数的用途和用法
举个例子,如果你想看看os.getcwd和os.popen的用法,你可以在terminal里如下操作:
[billc@bclinux ~]$ python3 进入python互交模式
Python 3.6.2 (default, Aug 20 2017, 10:04:14)
[GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-11)] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import os
>>> import sys
>>> help(os.getcwd) 用help()查看用法
Help on built-in function getcwd in module posix:
getcwd()
Return a unicode string representing the current working directory.
>>> help(os.popen) 用help()查看用法
Help on function popen in module os:
popen(cmd, mode='r', buffering=-1)
# Supply os.popen()
>>> os.getcwd() 还不明白?做个实验
'/home/billc' 打印了当前路径
>>> os.popen('ls') 再做个实验
<os._wrap_close object at 0x7f75fcda1208> 返回了一个对象
>>> os.popen('ls').readlines() 继续做实验
['Desktop\n', 'Documents\n', 'Downloads\n', 'Music\n', 'Pictures\n', 'Public\n', 'Videos\n'] 输出了ls命令的执行结果
还不懂怎么办?
-
python的书
-
百度、bing、google(如果你在国外、或者你有VPN/VPS)
-
知乎、博客
-
github上找些开源代码参考
-
身边的同学、同事、朋友
-
微信群
当然还可以阅读本公众号ExASIC的《Python在ASIC中的应用》系列文章。
疑难问题辨析
os.mkdir与os.makedirs
mkdir创建单个目录,而makedirs创建一串目录,类似shell命令make -p。
os.mkdir('a')
os.makedirs('a/b/c')
os.path.curdir、os.path.abspath、os.path.dirname、os.path.basename
curdir是属性,不是函数,返回一个字符串 ‘.’
abspath返回完整的路径。
dirname和basename的输入参数是完整路径,basename返回文件名,dirname返回文件名前面的路径。
os.path.abspath('file.txt') # /home/xxx/dir/file.txt
os.path.dirname('/home/xxx/dir/file.txt') # /home/xxx/dir
os.path.baseame('/home/xxx/dir/file.txt') # file.txt
os.path.dirname('../../file.txt') # ../../
所以说,dirname和basename并不会判断文件或路径是否真实存在,只是对提供的字符串做处理。
os.path.isdir、os.path.isfile、os.path.islink
这几个函数不只是字符串处理哦,文件或目录不存在时会报错。从名字上就可以看出它们的功能,判断是否是文件、目录、软链接,返回True和False。
os.path.split、os.path.splitext、os.path.join
split是把目录和文件分开,splitext是把文件名和后缀名分开,join把目录、文件用/组合成路径。
os.path.split('/home/xxx/dir/file.txt') # ['/home/xxx/dir', 'file.txt']
os.path.splitext('file.txt') # ['file', '.txt']
os.path.getsize、os.path.getatime、os.path.getctime、os.path.getmtime
os.path.getsize获取文件的大小。
os.path.getatime最后一次access时间,可以是创建、修改、读等。
os.path.getctime最后一次change时间,可以是修改、改变权限、改变所有者等。
os.path.getmtime最后一次modify时间,创建、修改等。
文件的更多信息可以通过os.stat()来获取。
写个实用的脚本/代码
比如,我们在仿真时,需要根据testcase名字建立一个仿真目录。
具体事项如下:
-
从命令行获取testcase名
-
确认项目根目录,获取当前目录的相对路径
-
用find命令获取testcase的类别
-
如果类别不存在,则新建类别目录,并产生Makefile
-
进入类别目录里
-
如果testcase目录不存在,则新建,并创建仿真脚本的软链接和Makefile
-
完毕后,打印成功提示
参考脚本:



更多python的文章
Python的函数(四):递归函数与匿名函数,函数的属性与标注
Python Developers Survey 2017 Results

写Python选什么编辑器,大家心里都有数了吧。(原来用Emacs的人这么少)
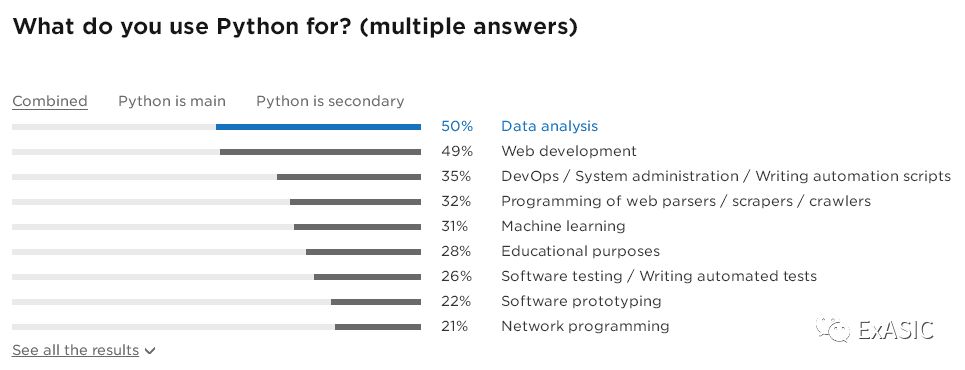
复制链接到浏览器查看完整《调查报告》(Python官网的调查报告):
https://www.jetbrains.com/research/python-developers-survey-2017/
广告时间

欢迎关注ExASIC

分享数字集成电路设计中的经验和方法
Sharing makes work smoother

文章评论