
-
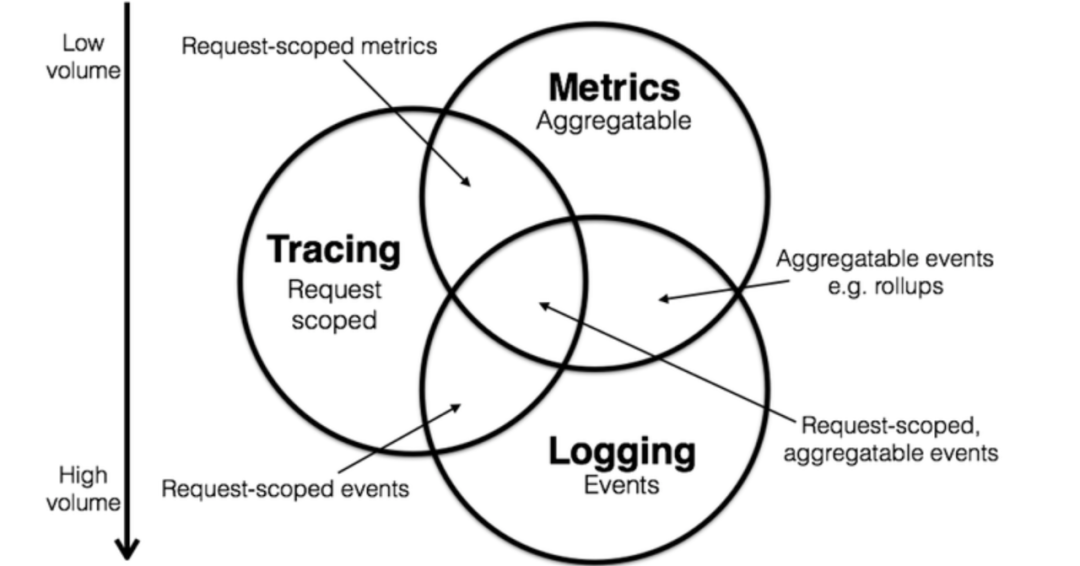
Lgging,展现的是应用运行而产生的事件或者程序在执行的过程中间产生的一些日志,可以详细解释系统的运行状态,但是存储和查询需要消耗大量的资源。所以往往使用过滤器减少数据量。
-
Metrics,是一种聚合数值,存储空间很小,可以观察系统的状态和趋势,但对于问题定位缺乏细节展示。这个时候使用等高线指标等多维数据结构来增强对于细节的表现力。例如统计一个服务的 TBS 的正确率、成功率、流量等,这是常见的针对单个指标或者某一个数据库的。
-
Tracing,面向的是请求,可以轻松分析出请求中异常点,但与Logging有相同的问题就是资源消耗较大。通常也需要通过采样的方式减少数据量。比如一次请求的范围,也就是从浏览器或者手机端发起的任何一次调用,一个流程化的东西,我们需要轨迹去追踪。

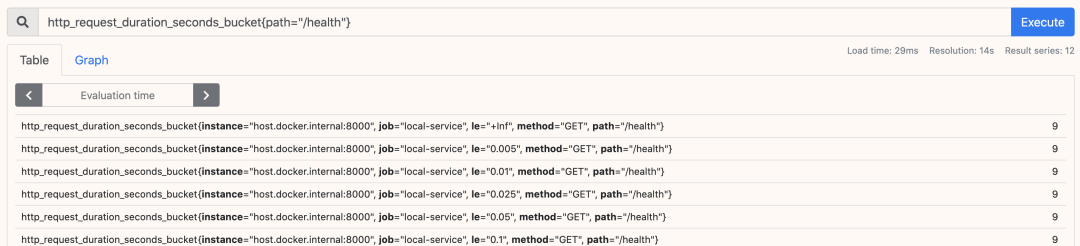
<metric name>{<label name>=<label value>, ...}
rate(http_requests_total[5m])
node_memory_MemFree
# HELP go_gc_duration_seconds A summary of the pause duration of garbage collection cycles.
# TYPE go_gc_duration_seconds summary
go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0"} 3.98e-05
go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0.25"} 5.31e-05
go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0.5"} 6.77e-05
go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0.75"} 0.0001428
go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="1"} 0.0008099
go_gc_duration_seconds_sum 0.0114183
go_gc_duration_seconds_count 85
# HELP prometheus_http_response_size_bytes Histogram of response size for HTTP requests.
# TYPE prometheus_http_response_size_bytes histogram
prometheus_http_response_size_bytes_bucket{handler="/",le="100"} 1
prometheus_http_response_size_bytes_bucket{handler="/",le="1000"} 1
prometheus_http_response_size_bytes_bucket{handler="/",le="10000"} 1
prometheus_http_response_size_bytes_bucket{handler="/",le="100000"} 1
prometheus_http_response_size_bytes_bucket{handler="/",le="1e+06"} 1
prometheus_http_response_size_bytes_bucket{handler="/",le="+Inf"} 1
prometheus_http_response_size_bytes_sum{handler="/"} 29
prometheus_http_response_size_bytes_count{handler="/"} 1

server := gin.New()
server.Use(middlewares.AccessLogger(), middlewares.Metric(), gin.Recovery())
server.GET("/health", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"message": "ok",
})
})
server.GET("/metrics", Monitor)
func Monitor(c *gin.Context) {
h := promhttp.Handler()
h.ServeHTTP(c.Writer, c.Request)
}
var (
//HTTPReqDuration metric:http_request_duration_seconds
HTTPReqDuration *prometheus.HistogramVec
//HTTPReqTotal metric:http_request_total
HTTPReqTotal *prometheus.CounterVec
// TaskRunning metric:task_running
TaskRunning *prometheus.GaugeVec
)
func init() {
// 监控接口请求耗时
// 指标类型是Histogram
HTTPReqDuration = prometheus.NewHistogramVec(prometheus.HistogramOpts{
Name: "http_request_duration_seconds",
Help: "http request latencies in seconds",
Buckets: nil,
}, []string{"method", "path"})
// "method"、"path" 是 label
// 监控接口请求次数
// 指标类型是 Counter
HTTPReqTotal = prometheus.NewCounterVec(prometheus.CounterOpts{
Name: "http_requests_total",
Help: "total number of http requests",
}, []string{"method", "path", "status"})
// "method"、"path"、"status" 是 label
// 监控当前在执行的task数量
// 监控类型是Gauge
TaskRunning = prometheus.NewGaugeVec(prometheus.GaugeOpts{
Name: "task_running",
Help: "current count of running task",
}, []string{"type", "state"})
// "type"、"state" 是 label
prometheus.MustRegister(
HTTPReqDuration,
HTTPReqTotal,
TaskRunning,
)
}
start := time.Now()
c.Next()
duration := float64(time.Since(start)) / float64(time.Second)
path := c.Request.URL.Path
// 请求数加1
controllers.HTTPReqTotal.With(prometheus.Labels{
"method": c.Request.Method,
"path": path,
"status": strconv.Itoa(c.Writer.Status()),
}).Inc()
// 记录本次请求处理时间
controllers.HTTPReqDuration.With(prometheus.Labels{
"method": c.Request.Method,
"path": path,
}).Observe(duration)
// 模拟新建任务
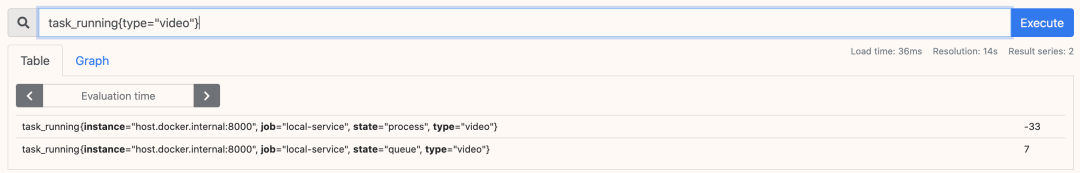
controllers.TaskRunning.With(prometheus.Labels{
"type": shuffle([]string{"video", "audio"}),
"state": shuffle([]string{"process", "queue"}),
}).Inc()
// 模拟任务完成
controllers.TaskRunning.With(prometheus.Labels{
"type": shuffle([]string{"video", "audio"}),
"state": shuffle([]string{"process", "queue"}),
}).Dec()
# 抓取间隔
scrape_interval: 5s
# 目标
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'prometheus'
static_configs:
- targets: ['prometheus:9090']
- job_name: 'local-service'
metrics_path: /metrics
static_configs:
- targets: ['host.docker.internal:8000']
↓↓ 点击"阅读原文" 【加入云技术社区】
相关阅读:
RightScale 2019年云状况调查报告:35% 的云支出被浪费「附50页PDF下载」
更多文章请关注

文章好看点这里[在看]?
文章评论