点击上方蓝色“石杉的架构笔记”,选择“设为星标”
回复“PDF”获取独家整理的学习资料!



长按扫描上方一元购买

来源:https://www.aneasystone.com/archives/2020/08/spring-cloud-gateway-current-limiting.html
-
Built on Spring Framework 5, Project Reactor and Spring Boot 2.0 -
Able to match routes on any request attribute -
Predicates and filters are specific to routes -
Hystrix Circuit Breaker integration -
Spring Cloud DiscoveryClient integration -
Easy to write Predicates and Filters -
Request Rate Limiting -
Path Rewriting
一、常见的限流场景
1.1 限流的对象
-
限制某个接口一分钟内最多请求 100 次 -
限制某个用户的下载速度最多 100KB/S -
限制某个用户同时只能对某个接口发起 5 路请求 -
限制某个 IP 来源禁止访问任何请求
1.2 限流的处理方式
-
拒绝服务 -
排队等待 -
服务降级
1.3 限流的架构
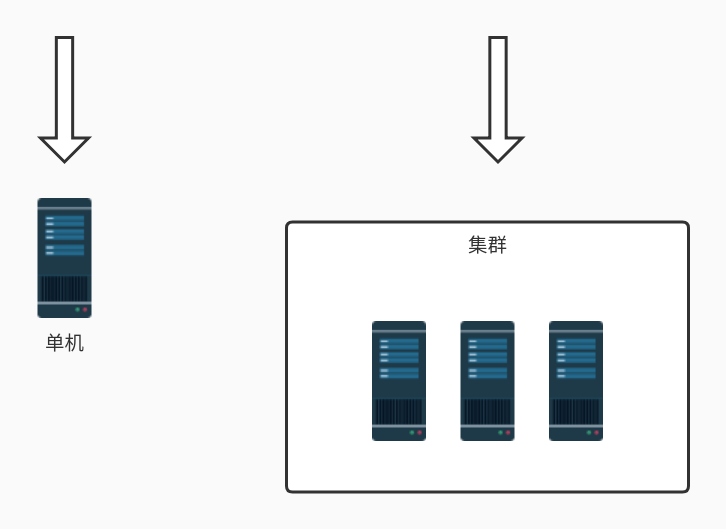 单机模式的限流非常简单,可以直接基于内存就可以实现,而集群模式的限流必须依赖于某个“中心化”的组件,比如网关或 Redis,从而引出两种不同的限流架构:网关层限流 和 中间件限流。
单机模式的限流非常简单,可以直接基于内存就可以实现,而集群模式的限流必须依赖于某个“中心化”的组件,比如网关或 Redis,从而引出两种不同的限流架构:网关层限流 和 中间件限流。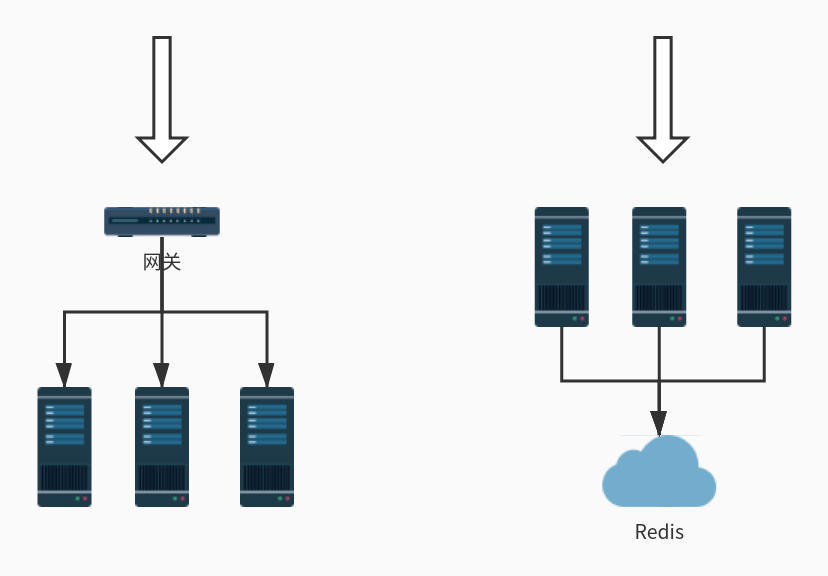
二、常见的限流算法
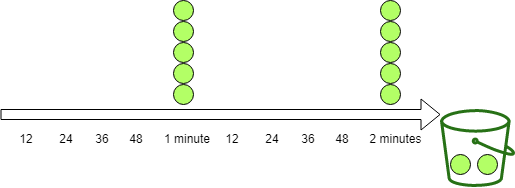
2.1 固定窗口算法(Fixed Window)
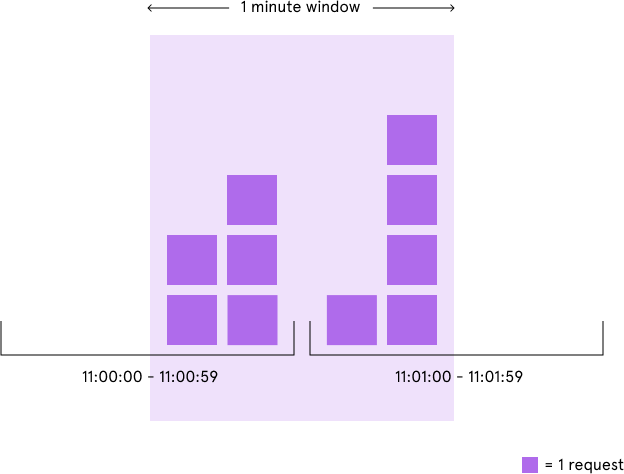
2.2 滑动窗口算法(Rolling Window 或 Sliding Window)
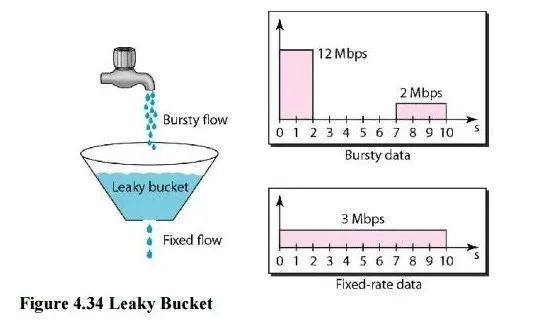
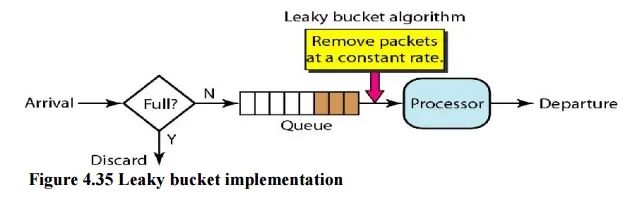
2.3 漏桶算法(Leaky Bucket)
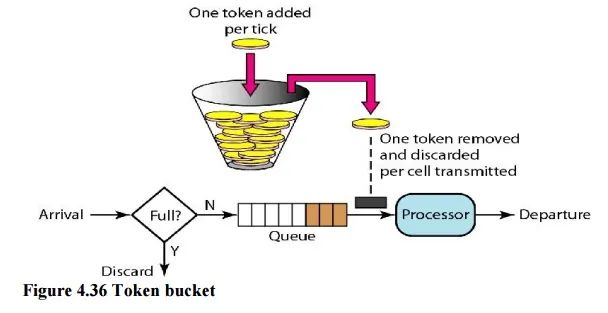
2.4 令牌桶算法(Token Bucket)
-
生成令牌:假设有一个装令牌的桶,最多能装 M 个,然后按某个固定的速度(每秒 r 个)往桶中放入令牌,桶满时不再放入; -
消费令牌:我们的每次请求都需要从桶中拿一个令牌才能放行,当桶中没有令牌时即触发限流,这时可以将请求放入一个缓冲队列中排队等待,或者直接拒绝;
1public class TokenBucket {
2
3 private final long capacity;
4 private final double refillTokensPerOneMillis;
5 private double availableTokens;
6 private long lastRefillTimestamp;
7
8 public TokenBucket(long capacity, long refillTokens, long refillPeriodMillis) {
9 this.capacity = capacity;
10 this.refillTokensPerOneMillis = (double) refillTokens / (double) refillPeriodMillis;
11 this.availableTokens = capacity;
12 this.lastRefillTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
13 }
14
15 synchronized public boolean tryConsume(int numberTokens) {
16 refill();
17 if (availableTokens < numberTokens) {
18 return false;
19 } else {
20 availableTokens -= numberTokens;
21 return true;
22 }
23 }
24
25 private void refill() {
26 long currentTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
27 if (currentTimeMillis > lastRefillTimestamp) {
28 long millisSinceLastRefill = currentTimeMillis - lastRefillTimestamp;
29 double refill = millisSinceLastRefill * refillTokensPerOneMillis;
30 this.availableTokens = Math.min(capacity, availableTokens + refill);
31 this.lastRefillTimestamp = currentTimeMillis;
32 }
33 }
34}
1TokenBucket limiter = new TokenBucket(100, 100, 1000);
三、一些开源项目
3.1 Guava 的 RateLimiter
1RateLimiter limiter = RateLimiter.create(5);
1System.out.println(limiter.acquire());
2System.out.println(limiter.acquire());
3System.out.println(limiter.acquire());
4System.out.println(limiter.acquire());
10.0
20.198239
30.196083
40.200609
1RateLimiter limiter = RateLimiter.create(5);
2System.out.println(limiter.acquire(10));
3System.out.println(limiter.acquire(1));
4System.out.println(limiter.acquire(1));
10.0
21.997428
30.192273
40.200616
1RateLimiter limiter = RateLimiter.create(2, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
2System.out.println(limiter.acquire(1));
3System.out.println(limiter.acquire(1));
4System.out.println(limiter.acquire(1));
5System.out.println(limiter.acquire(1));
6System.out.println(limiter.acquire(1));
10.0
21.329289
30.994375
40.662888
50.501287
3.2 Bucket4j
-
Bucket -
Bandwidth -
Refill
1Bucket bucket = Bucket4j.builder().addLimit(limit).build();
2if(bucket.tryConsume(1)) {
3 System.out.println("ok");
4} else {
5 System.out.println("error");
6}
1Bandwidth limit = Bandwidth.simple(10, Duration.ofMinutes(1));
1Refill filler = Refill.greedy(5, Duration.ofMinutes(1));
2Bandwidth limit = Bandwidth.classic(10, filler);
1Refill filler = Refill.intervally(5, Duration.ofMinutes(1));
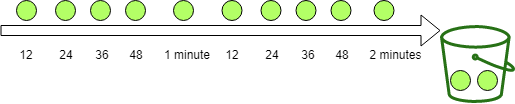
-
基于令牌桶算法 -
高性能,无锁实现 -
不存在精度问题,所有计算都是基于整型的 -
支持通过符合 JCache API 规范的分布式缓存系统实现分布式限流 -
支持为每个 Bucket 设置多个 Bandwidth -
支持同步和异步 API -
支持可插拔的监听 API,用于集成监控和日志 -
不仅可以用于限流,还可以用于简单的调度
3.3 Resilience4j

1// 创建一个 Bulkhead,最大并发量为 150
2BulkheadConfig bulkheadConfig = BulkheadConfig.custom()
3 .maxConcurrentCalls(150)
4 .maxWaitTime(100)
5 .build();
6Bulkhead bulkhead = Bulkhead.of("backendName", bulkheadConfig);
7
8// 创建一个 RateLimiter,每秒允许一次请求
9RateLimiterConfig rateLimiterConfig = RateLimiterConfig.custom()
10 .timeoutDuration(Duration.ofMillis(100))
11 .limitRefreshPeriod(Duration.ofSeconds(1))
12 .limitForPeriod(1)
13 .build();
14RateLimiter rateLimiter = RateLimiter.of("backendName", rateLimiterConfig);
15
16// 使用 Bulkhead 和 RateLimiter 装饰业务逻辑
17Supplier<String> supplier = () -> backendService.doSomething();
18Supplier<String> decoratedSupplier = Decorators.ofSupplier(supplier)
19 .withBulkhead(bulkhead)
20 .withRateLimiter(rateLimiter)
21 .decorate();
22
23// 调用业务逻辑
24Try<String> try = Try.ofSupplier(decoratedSupplier);
25assertThat(try.isSuccess()).isTrue();
3.4 其他
-
https://github.com/mokies/ratelimitj -
https://github.com/wangzheng0822/ratelimiter4j -
https://github.com/wukq/rate-limiter -
https://github.com/marcosbarbero/spring-cloud-zuul-ratelimit -
https://github.com/onblog/SnowJena -
https://gitee.com/zhanghaiyang/spring-boot-starter-current-limiting -
https://github.com/Netflix/concurrency-limits
四、在网关中实现限流
4.1 实现单机请求频率限流
Spring Cloud Gateway 中定义了关于限流的一个接口 RateLimiter,如下:
1public interface RateLimiter<C> extends StatefulConfigurable<C> {
2 Mono<RateLimiter.Response> isAllowed(String routeId, String id);
3}
1@Override
2public GatewayFilter apply(Config config) {
3 // 从配置中得到 KeyResolver
4 KeyResolver resolver = getOrDefault(config.keyResolver, defaultKeyResolver);
5 // 从配置中得到 RateLimiter
6 RateLimiter<Object> limiter = getOrDefault(config.rateLimiter,
7 defaultRateLimiter);
8 boolean denyEmpty = getOrDefault(config.denyEmptyKey, this.denyEmptyKey);
9 HttpStatusHolder emptyKeyStatus = HttpStatusHolder
10 .parse(getOrDefault(config.emptyKeyStatus, this.emptyKeyStatusCode));
11
12 return (exchange, chain) -> resolver.resolve(exchange).defaultIfEmpty(EMPTY_KEY)
13 .flatMap(key -> {
14 // 通过 KeyResolver 得到 key,作为唯一标识 id 传入 isAllowed() 方法
15 if (EMPTY_KEY.equals(key)) {
16 if (denyEmpty) {
17 setResponseStatus(exchange, emptyKeyStatus);
18 return exchange.getResponse().setComplete();
19 }
20 return chain.filter(exchange);
21 }
22 // 获取当前路由 ID,作为 routeId 参数传入 isAllowed() 方法
23 String routeId = config.getRouteId();
24 if (routeId == null) {
25 Route route = exchange
26 .getAttribute(ServerWebExchangeUtils.GATEWAY_ROUTE_ATTR);
27 routeId = route.getId();
28 }
29 return limiter.isAllowed(routeId, key).flatMap(response -> {
30
31 for (Map.Entry<String, String> header : response.getHeaders()
32 .entrySet()) {
33 exchange.getResponse().getHeaders().add(header.getKey(),
34 header.getValue());
35 }
36 // 请求允许,直接走到下一个 filter
37 if (response.isAllowed()) {
38 return chain.filter(exchange);
39 }
40 // 请求被限流,返回设置的 HTTP 状态码(默认是 429)
41 setResponseStatus(exchange, config.getStatusCode());
42 return exchange.getResponse().setComplete();
43 });
44 });
45}
1public interface KeyResolver {
2 Mono<String> resolve(ServerWebExchange exchange);
3}
1public interface KeyResolver {
2 Mono<String> resolve(ServerWebExchange exchange);
3}
4比如下面的 HostAddrKeyResolver 可以根据 IP 来限流:
5public class HostAddrKeyResolver implements KeyResolver {
6 @Override
7 public Mono<String> resolve(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
8 return Mono.just(exchange.getRequest().getRemoteAddress().getAddress().getHostAddress());
9 }
10}
我们继续看 Spring Cloud Gateway 的代码发现,RateLimiter 接口只提供了一个实现类 RedisRateLimiter:
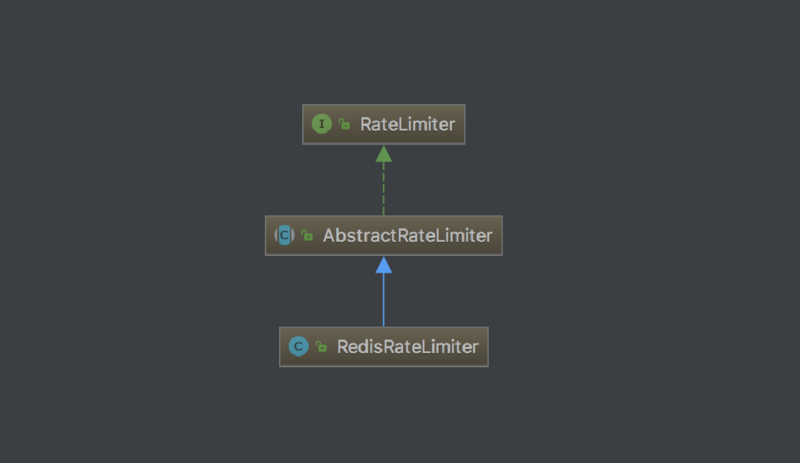
很显然是基于 Redis 实现的限流,虽说通过 Redis 也可以实现单机限流,但是总感觉有些大材小用,而且对于那些没有 Redis 的环境很不友好。所以,我们要实现真正的本地限流。
1public Mono<Response> isAllowed(String routeId, String id) {
2 Config routeConfig = loadConfiguration(routeId);
3
4 // How many requests per second do you want a user to be allowed to do?
5 int replenishRate = routeConfig.getReplenishRate();
6
7 // How many seconds for a token refresh?
8 int refreshPeriod = routeConfig.getRefreshPeriod();
9
10 // How many tokens are requested per request?
11 int requestedTokens = routeConfig.getRequestedTokens();
12
13 final io.github.resilience4j.ratelimiter.RateLimiter rateLimiter = RateLimiterRegistry
14 .ofDefaults()
15 .rateLimiter(id, createRateLimiterConfig(refreshPeriod, replenishRate));
16
17 final boolean allowed = rateLimiter.acquirePermission(requestedTokens);
18 final Long tokensLeft = (long) rateLimiter.getMetrics().getAvailablePermissions();
19
20 Response response = new Response(allowed, getHeaders(routeConfig, tokensLeft));
21 return Mono.just(response);
22}
有意思的是,这个类 还有一个早期版本,是基于 Bucket4j 实现的:
1public Mono<Response> isAllowed(String routeId, String id) {
2
3 Config routeConfig = loadConfiguration(routeId);
4
5 // How many requests per second do you want a user to be allowed to do?
6 int replenishRate = routeConfig.getReplenishRate();
7
8 // How much bursting do you want to allow?
9 int burstCapacity = routeConfig.getBurstCapacity();
10
11 // How many tokens are requested per request?
12 int requestedTokens = routeConfig.getRequestedTokens();
13
14 final Bucket bucket = bucketMap.computeIfAbsent(id,
15 (key) -> createBucket(replenishRate, burstCapacity));
16
17 final boolean allowed = bucket.tryConsume(requestedTokens);
18
19 Response response = new Response(allowed,
20 getHeaders(routeConfig, bucket.getAvailableTokens()));
21 return Mono.just(response);
22}
4.2 实现分布式请求频率限流
1local tokens_key = KEYS[1]
2local timestamp_key = KEYS[2]
3
4local rate = tonumber(ARGV[1])
5local capacity = tonumber(ARGV[2])
6local now = tonumber(ARGV[3])
7local requested = tonumber(ARGV[4])
8
9local fill_time = capacity/rate
10local ttl = math.floor(fill_time*2)
11
12local last_tokens = tonumber(redis.call("get", tokens_key))
13if last_tokens == nil then
14 last_tokens = capacity
15end
16
17local last_refreshed = tonumber(redis.call("get", timestamp_key))
18if last_refreshed == nil then
19 last_refreshed = 0
20end
21
22local delta = math.max(0, now-last_refreshed)
23local filled_tokens = math.min(capacity, last_tokens+(delta*rate))
24local allowed = filled_tokens >= requested
25local new_tokens = filled_tokens
26local allowed_num = 0
27if allowed then
28 new_tokens = filled_tokens - requested
29 allowed_num = 1
30end
31
32if ttl > 0 then
33 redis.call("setex", tokens_key, ttl, new_tokens)
34 redis.call("setex", timestamp_key, ttl, now)
35end
36
37return { allowed_num, new_tokens }
1spring:
2 cloud:
3 gateway:
4 routes:
5 - id: test
6 uri: http://httpbin.org:80/get
7 filters:
8 - name: RequestRateLimiter
9 args:
10 key-resolver: '#{@hostAddrKeyResolver}'
11 redis-rate-limiter.replenishRate: 1
12 redis-rate-limiter.burstCapacity: 3
1@Bean
2public RouteLocator myRoutes(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {
3 return builder.routes()
4 .route(p -> p
5 .path("/get")
6 .filters(filter -> filter.requestRateLimiter()
7 .rateLimiter(RedisRateLimiter.class, rl -> rl.setBurstCapacity(3).setReplenishRate(1)).and())
8 .uri("http://httpbin.org:80"))
9 .build();
10}
4.3 实现单机并发量限流
1public class SemaphoreTest {
2
3 private static ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);
4 private static Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(10);
5
6 public static void main(String[] args) {
7 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
8 threadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
9 @Override
10 public void run() {
11 try {
12 semaphore.acquire();
13 System.out.println("Request processing ...");
14 semaphore.release();
15 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
16 e.printStack();
17 }
18 }
19 });
20 }
21 threadPool.shutdown();
22 }
23}
1public class AtomicLongTest {
2
3 private static ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);
4 private static AtomicLong atomic = new AtomicLong();
5
6 public static void main(String[] args) {
7 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
8 threadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
9 @Override
10 public void run() {
11 try {
12 if(atomic.incrementAndGet() > 10) {
13 System.out.println("Request rejected ...");
14 return;
15 }
16 System.out.println("Request processing ...");
17 atomic.decrementAndGet();
18 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
19 e.printStack();
20 }
21 }
22 });
23 }
24 threadPool.shutdown();
25 }
26}
1semaphore.acquire();
2System.out.println("Request processing ...");
3semaphore.release();
1try {
2 semaphore.acquire();
3 System.out.println("Request processing ...");
4} catch (InterruptedException e) {
5 e.printStack();
6} finally {
7 semaphore.release();
8}
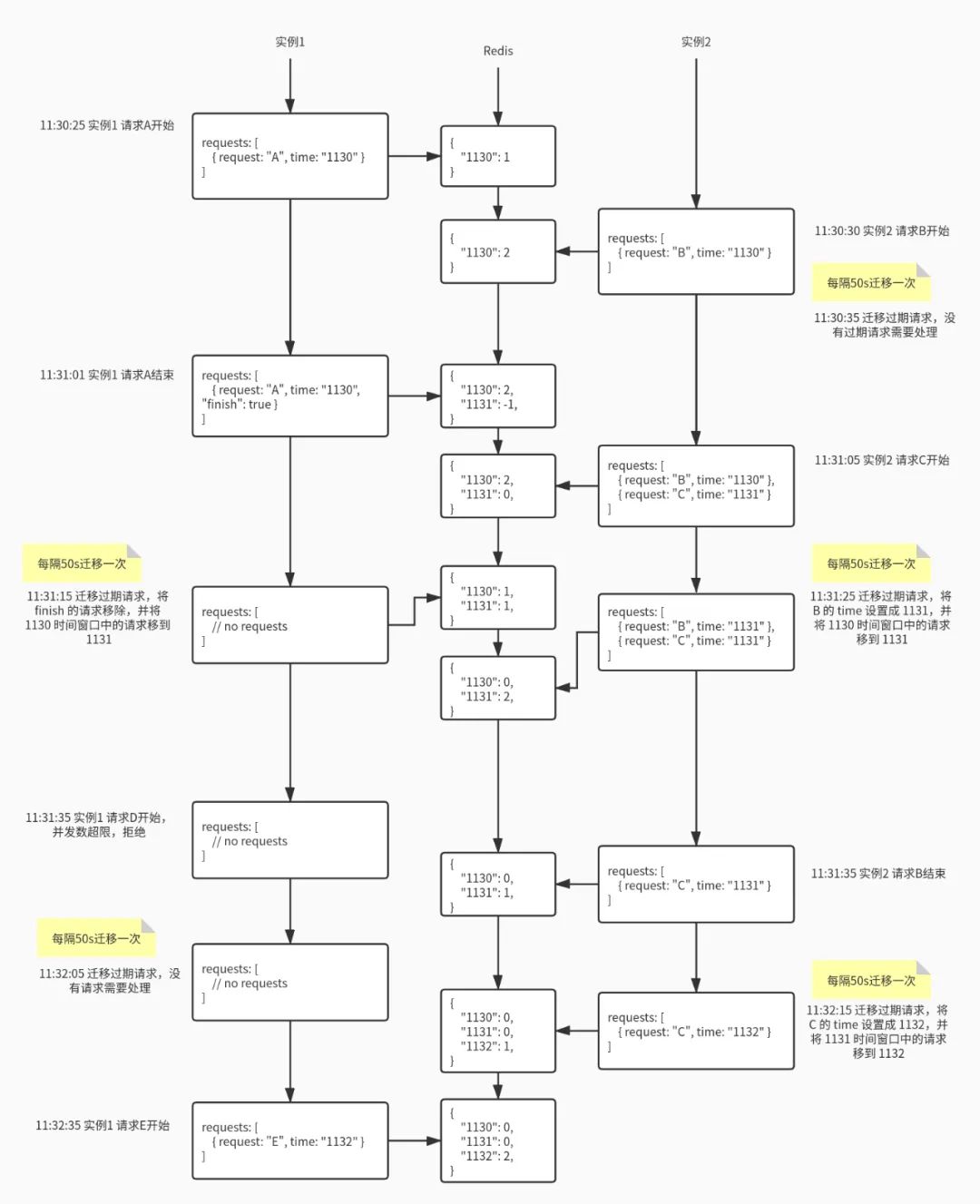
-
请求结束时,直接在 Redis 中当前时间窗口减一即可,就算是负数也没关系。请求列表中的该请求不用急着删除,可以打上结束标记,在迁移线程中统一删除(当然,如果请求的开始时间和结束时间在同一个窗口,可以直接删除); -
迁移的时间间隔要小于时间窗口,一般设置为 30s; -
Redis 中的 key 一定要设置 TTL,时间至少为 2 个时间窗口,一般设置为 3 分钟; -
迁移过程涉及到“从上一个时间窗口减”和“在当前时间窗口加”两个操作,要注意操作的原子性; -
获取当前并发量可以通过 MGET 一次性读取两个时间窗口的值,不用 GET 两次; -
获取并发量和判断并发量是否超限,这个过程也要注意操作的原子性。
总结
参考
-
微服务网关实战——Spring Cloud Gateway -
《亿级流量网站架构核心技术》张开涛 -
聊聊高并发系统之限流特技 -
架构师成长之路之限流 -
微服务接口限流的设计与思考 -
常用4种限流算法介绍及比较 -
来谈谈限流-从概念到实现 -
高并发下的限流分析 -
计数器算法 -
基于Redis的限流系统的设计 -
API 调用次数限制实现 -
Techniques to Improve QoS -
An alternative approach to rate limiting -
Scaling your API with rate limiters -
Brief overview of token-bucket algorithm -
Rate limiting Spring MVC endpoints with bucket4j -
Rate Limiter Internals in Resilience4j -
高可用框架Resilience4j使用指南 -
阿里巴巴开源限流系统 Sentinel 全解析 -
spring cloud gateway 之限流篇 -
服务容错模式 -
你的API会自适应「弹性」限流吗?

文章评论