下面的代码会在页面上输出 Hello World,但是在这个
new Vue()到页面渲染之间,到底发生了什么。这篇文章希望通过最简单的例子,去了解 Vue 源码过程。这里分析的源码版本是Vue.version = '1.0.20'
<div id="mountNode">{{message}}</div>var vm = new Vue({
el: '#mountNode',
data: function () {
return {
message: 'Hello World'
};
}
});这篇文章将要解决几个问题:
-
new Vue() 的过程中,内部到底有哪些步骤
-
如何收集依赖
-
如何计算表达式
-
如何表达式的值如何反应在 DOM 上的
简单来说过程是这样的:
-
observe:把{message: ‘Hello World’}变成是 reactive 的
-
compile:compileTextNode “{{message}}”,解析出指令(directive = v-text)和表达式(expression = message),创建 fragment(new TextNode)准备替换
-
link:实例化 directive,将创建的 fragment 和 directive 链接起来,将 fragment 替换在 DOM 上
-
bind:通过 directive 对应的 watcher 获取依赖(message)的值(“Hello World”),v-text去 update 值到 fragment 上
详细过程,接着往下看。
构造函数
文件路径:src/instance/vue.js
function Vue (options) {
this._init(options)
}初始化
这里只拿对例子理解最关键的步骤分析。
文件路径:src/instance/internal/init.js
Vue.prototype._init = function (options) {
... // merge options.
options = this.$options = mergeOptions(
this.constructor.options,
options,
this
)
...
// initialize data observation and scope inheritance.
this._initState()
...
// if `el` option is passed, start compilation.
if (options.el) {
this.$mount(options.el)
}
}merge options
mergeOptions()定义在 src/util/options.js 文件中,这里主要定义 options 中各种属性的合并(merge),例如:props, methods, computed, watch等。另外,这里还定义了每种属性 merge 的默认算法(strategy),这些 strategy 都可以配置的,参考 Custom Option Merge Strategy。
在本文的例子中,主要是 data 选项的 merge,在 merge 之后,放到$options.data中,基本相当于下面这样:
vm.$options.data = function mergedInstanceDataFn () {
var parentVal = undefined
// 这里就是在我们定义的options中的data
var childVal = function () {
return {
message: 'Hello World'
}
}
// data function绑定vm实例后执行,执行结果: {message: 'Hello World'}
var instanceData = childVal.call(vm)
// 对象之间的merge,类似$.extend,结果肯定就是:{message: 'Hello World'}
return mergeData(instanceData, parentVal)
}init data
_initData()发生在_initState()中,主要做了两件事:
-
代理 data 中的属性
-
observe data
文件路径:src/instance/internal/state.js
Vue.prototype._initState = function () {
this._initProps()
this._initMeta()
this._initMethods()
this._initData() // 这里
this._initComputed()
}属性代理(proxy)
把 data 的结果赋值给内部属性:
文件路径:src/instance/internal/state.js
var dataFn = this.$options.data // 上面我们得到的mergedInstanceDataFn函数
var data = this._data = dataFn ? dataFn() : {}代理(proxy)data中的属性到_data,使得vm.message === vm._data.message:
文件路径:src/instance/internal/state.js
/**
* Proxy a property, so that
* vm.prop === vm._data.prop
*/
Vue.prototype._proxy = function (key) {
if (!isReserved(key)) {
var self = this
Object.defineProperty(self, key, {
configurable: true,
enumerable: true,
get: function proxyGetter () {
return self._data[key]
},
set: function proxySetter (val) {
self._data[key] = val
}
})
}
}observe
这里是我们的第一个重点,observe 过程。在_initData()最后,调用了observe(data, this)对数据进行 observe。在 hello world 例子里,observe()函数主要是针对{message: 'Hello World'}创建了Observer对象。
文件路径:src/observer/index.js
var ob = new Observer(value) // value = data = {message:'Hello World'}在observe()函数中还做了些能否 observe 的条件判断,这些条件有:
-
没有被 observe 过(observe 过的对象都会被添加
__ob__属性) -
只能是 plain object(
toString.call(ob) === "[object Object]")或者数组 -
不能是 Vue 实例(
obj._isVue !== true) -
object 是 extensible 的(
Object.isExtensible(obj) === true)
Observer
官网的 Reactivity in Depth 上有这么句话:
When you pass a plain JavaScript object to a Vue instance as its data option, Vue.js will walk through all of its properties and convert them to getter/setters
The getter/setters are invisible to the user, but under the hood they enable Vue.js to perform dependency-tracking and change-notification when properties are accessed or modified
Observer 就是干这个事情的,使 data 变成“发布者”,watcher 是订阅者,订阅 data 的变化。
在例子中,创建 observer 的过程是:
-
new Observer({message: 'Hello World'}) -
实例化一个 Dep 对象,用来收集依赖
-
walk(
Observer.prototype.walk())数据的每一个属性,这里只有 message -
将属性变成 reactive 的 (
Observer.protoype.convert())
convert()里调用了defineReactive(),给 data 的 message 属性添加 reactiveGetter 和 reactiveSetter
文件路径:src/observer/index.js
export function defineReactive (obj, key, value) {
... Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter () {
... if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend() // 这里是收集依赖
...
} return value
},
set: function reactiveSetter (newVal) {
... if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal)
} else {
val = newVal
}
...
dep.notify() // 这里是notify观察这个数据的依赖(watcher)
}
})
}关于依赖收集和 notify,主要是Dep类
文件路径:src/observer/dep.js
export default function Dep () { this.id = uid++ this.subs = []
}这里的 subs 是保存着订阅者(即 watcher)的数组,当被观察数据发生变化时,即被调用 setter,那么dep.notify()就循环这里的订阅者,分别调用他们的 update 方法。
但是在 getter 收集依赖的代码里,并没有看到 watcher 被添加到 subs 中,什么时候添加进去的呢?这个问题在讲到 Watcher 的时候再回答。
mount node
按照生命周期图上,observe data 和一些 init 之后,就是$mount了,最主要的就是_compile。
文件路径:src/instance/api/lifecycle.js
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (el) {
...
this._compile(el)
...
}_compile里分两步:compile 和 link
compile
compile 过程是分析给定元素(el)或者模版(template),提取指令(directive)和创建对应离线的 DOM 元素(document fragment)。
文件路径:src/instance/internal/lifecycle.js
Vue.prototype._compile = function (el) {
...
var rootLinker = compileRoot(el, options, contextOptions)
...
var rootUnlinkFn = rootLinker(this, el, this._scope)
...
var contentUnlinkFn = compile(el, options)(this, el)
...
}例子中 compile #mountNode 元素,大致过程如下:
-
compileRoot:由于root node(
<div id="mountNode"></div>)本身没有任何指令,所以这里 compile 不出什么东西 -
compileChildNode:mountNode 的子 node,即内容为”{{message}}”的 TextNode
-
compileTextNode:
3.1 parseText:其实就是 tokenization(标记化:从字符串中提取符号,语句等有意义的元素),得到的结果是 tokens
3.2 processTextToken:从 tokens 中分析出指令类型,表达式和过滤器,并创建新的空的 TextNode
3.3 创建 fragment,将新的 TextNode append 进去
parseText 的时候,通过正则表达式(/\{\{\{(.+?)\}\}\}|\{\{(.+?)\}\}/g)匹配字符串”{{message}}”,得出的 token 包含这些信息:“这是个 tag,而且是文本(text)而非 HTML 的 tag,不是一次性的插值(one-time interpolation),tag 的内容是”message””。这里用来做匹配的正则表达式是会根据 delimiters 和 unsafeDelimiters 的配置动态生成的。
processTextToken 之后,其实就得到了创建指令需要的所有信息:指令类型 v-text,表达式”message”,过滤器无,并且该指令负责跟进的 DOM 是新创建的 TextNode。接下来就是实例化指令了。
link
每个 compile 函数之后都会返回一个 link function(linkFn)。linkFn 就是去实例化指令,将指令和新建的元素 link 在一起,然后将元素替换到 DOM tree 中去。
每个 linkFn 函数都会返回一个 unlink function(unlinkFn)。unlinkFn 是在 vm 销毁的时候用的,这里不介绍。
实例化 directive:new Directive(description, vm, el)
description是 compile 结果 token 中保存的信息,内容如下:
description = {
name: 'text', // text指令
expression: 'message',
filters: undefined,
def: vTextDefinition
}def 属性上的是 text 指令的定义(definition),和 Custome Directive 一样,text 指令也有 bind 和 update 方法,其定义如下:
文件路径:src/directives/public/text.js
export default {
bind () {
this.attr = this.el.nodeType === 3
? 'data'
: 'textContent'
},
update (value) {
this.el[this.attr] = _toString(value)
}
}new Directive()构造函数里面只是一些内部属性的赋值,真正的绑定过程还需要调用Directive.prototype._bind,它是在 Vue 实例方法_bindDir()中被调用的。
在 _bind 里面,会创建 watcher,并第一次通过 watcher 去获得表达式”message”的计算值,更新到之前新建的 TextNode 中去,完成在页面上渲染”Hello World”。
watcher
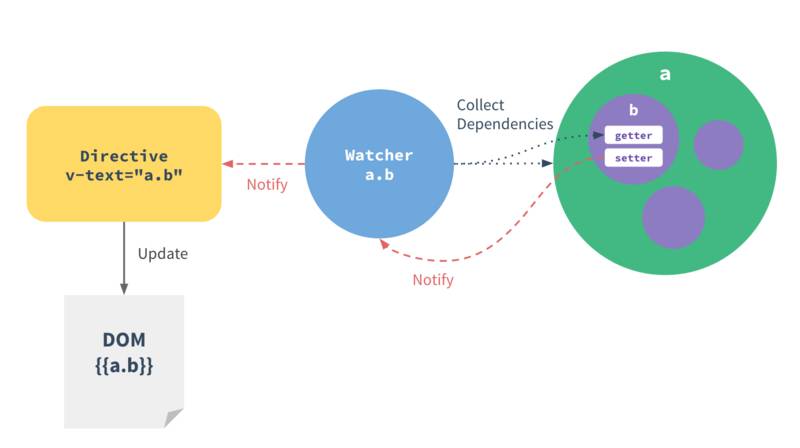
For every directive / data binding in the template, there will be a corresponding watcher object, which records any properties “touched” during its evaluation as dependencies. Later on when a dependency’s setter is called, it triggers the watcher to re-evaluate, and in turn causes its associated directive to perform DOM updates.
每个与数据绑定的 directive 都有一个 watcher,帮它监听表达式的值,如果发生变化,则通知它 update 自己负责的 DOM。一直说的 dependency collection 就在这里发生。
Directive.prototype._bind() 里面,会new Watcher(expression, update),把表达式和 directive 的 update 方法传进去。
Watcher 会去parseExpression:
文件路径:src/parsers/expression.js
export function parseExpression (exp, needSet) {
exp = exp.trim()
// try cache
var hit = expressionCache.get(exp)
if (hit) {
if (needSet && !hit.set) {
hit.set = compileSetter(hit.exp)
}
return hit
}
var res = { exp: exp }
res.get = isSimplePath(exp) && exp.indexOf('[') < 0
// optimized super simple getter
? makeGetterFn('scope.' + exp)
// dynamic getter
: compileGetter(exp)
if (needSet) {
res.set = compileSetter(exp)
}
expressionCache.put(exp, res)
return res
}这里的 expression 是”message”,单一变量,被认为是简单的数据访问路径(simplePath)。simplePath 的值如何计算,怎么通过”message”字符串获得 data.message的值呢?
获取字符串对应的变量的值,除了用 eval,还可以用 Function。上面的makeGetterFn('scope.' + exp)返回:
var getter = new Function('scope', 'return ' + body + ';') // new Function('scope', 'return scope.message;')Watch.prototype.get() 获取表达式值的时候,
var scope = this.vm
getter.call(scope, scope) // 即执行vm.message由于initState时对数据进行了代理(proxy),这里的vm.message即为vm._data.message,即是data选项中定义的”Hello World”。
值拿到了,那什么时候将message设为依赖的呢?这就要结合前面observe data里说到的reactiveGetter了。
文件路径:src/watcher.js
Watcher.prototype.get = function () { this.beforeGet() // -> Dep.target = this
var scope = this.scope || this.vm
...
var value value = this.getter.call(scope, scope)
...
this.afterGet() // -> Dep.target = null
return value
}watcher 获取表达式的值分三步:
-
beforeGet:设置
Dep.target = this -
调用表达式的 getter,读取(getter)vm.message 的值,进入了 message 的 reactiveGetter,由于 Dep.target 有值,因此执行了
dep.depend()将 target,即当前 watcher,收入 dep.subs 数组里 -
afterGet:设置
Dep.target = null
这里值得注意的是Dep.target,由于 JS 的单线程特性,同一时刻只能有一个 watcher 去 get 数据的值,所以 target 在全局下只需要有一个就可以了。
文件路径:src/observer/dep.js
// the current target watcher being evaluated.
// this is globally unique because there could be only one
// watcher being evaluated at any time.
Dep.target = null就这样,指令通过 watcher,去 touch 了表达式中涉及到的数据,同时被该数据(reactive data)保存为其变化的订阅者(subscriber),数据变化时,通过 dep.notify() -> watcher.update() -> directive.update() -> textDirective.update(),完成 DOM 的更新。
到这里,“Hello World”怎么渲染到页面上的过程基本就结束了。这里针对最简单的使用,挑选了最核心的步骤进行分析,更多内部细节,后面慢慢分享。
对文章内容感兴趣的读者,可以通过下方的「阅读原文」进行查看关注哦。
文章评论